Creating a WhatsApp clone for Android is an exciting project for any developer looking to dive into real-time messaging and social app development. WhatsApp, with its seamless chat, video calls, and media sharing features, has set a high standard for messaging apps. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps to build a similar app, using modern tools and technologies like Flutter, Firebase, or native Android development. Whether you’re aiming to build a simple chat app or incorporate advanced features like end-to-end encryption, real-time notifications, and media sharing, this guide will help you get started on your path for Whatsapp clone.
What is a WhatsApp Clone?
A WhatsApp clone is a messaging application designed to replicate the core functionalities of WhatsApp, including text messaging, voice and video calls, multimedia sharing, and group chats. These clones are often built by developers or companies looking to create a similar platform with added customizations, catering to niche markets or specific user needs.
Understanding the Key Features of WhatsApp
WhatsApp, the popular messaging application, is packed with a wide range of key features that make it a preferred choice for communication. Here are the key features of WhatsApp:
- Real-Time Messaging: The core feature of any WhatsApp clone is the ability to send and receive real-time messages using internet connectivity.
- Voice and Video Calls: Offering voice and video calling options, either one-on-one or in groups, is essential for a modern communication app.
- End-to-end Encryption: Ensuring user privacy with end-to-end encryption to protect chats and calls is a crucial aspect of any WhatsApp-like app.
- Multimedia Sharing: Users can send images, videos, documents, and voice notes seamlessly through the app.
- Group Chats: Support for group chats, allowing multiple users to communicate in a single conversation.
- Push Notifications: Real-time alerts for incoming messages, calls, or multimedia is necessary to keep users engaged.
Why Build a WhatsApp Clone?
With communication apps like WhatsApp dominating the market, a WhatsApp clone offers an opportunity to create a customized messaging platform tailored to specific needs. Here’s why building one could be valuable:
1. Customization for Specific Needs
Building a WhatsApp clone allows developers to customize the app to meet unique needs that mainstream messaging platforms like WhatsApp may not address. Businesses can integrate specialized features such as appointment scheduling, advanced file-sharing, or internal communication tools, all designed to enhance the app’s usability for their specific industry.
2. Targeting Specific Niches
A WhatsApp clone provides the flexibility to target niche markets or industries. For example, educational institutions could use a clone to enable better communication between teachers, students, and parents, with additional features like online assignment submission. Similarly, healthcare providers can utilize secure messaging between doctors and patients for telemedicine, making the app suitable for specific industries.
3. Branding Opportunities
Developing a WhatsApp clone offers full control over branding and user experience. Businesses can create a fully branded interface with their own logos, color schemes, and design elements, allowing them to stand out and provide a unique experience that differentiates their product from generic messaging platforms.
4. Monetization Potential
A WhatsApp clone provides opportunities for monetization through premium features like enhanced security, cloud storage, or advanced tools. Businesses can adopt subscription models or in-app purchases, offering exclusive features or ad-free experiences, creating additional revenue streams while catering to specific user needs.
Challenges of Building WhatsApp Clone
Building a WhatsApp clone with messaging API can be an enticing endeavor, but it comes with its fair share of challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developers looking to undertake such a project. Here are the key challenges of building a WhatsApp clone:
1. Scalability
WhatsApp has millions of active users, and ensuring that the clone can handle a large user base without performance issues is a significant challenge.
2. Security
Implementing end-to-end encryption, which is a critical feature of WhatsApp, requires expertise in cryptography and secure communication protocols.
3. Real-time Communication
Building a real-time messaging system that delivers messages instantly and reliably can be complex, as it involves handling push notifications, message queues, and network optimizations.
4. Cross-Platform Compatibility
WhatsApp is a cross-platform messaging app that is available on iOS, Android, and desktop devices. Copying the app’s features and functionality to create a clone can be technically challenging, as it requires developers to account for the differences between the different platforms.
5. User Experience
Replicating the smooth and intuitive user experience of WhatsApp requires meticulous attention to design, usability, and performance optimization.
6. Server Infrastructure
Developing a robust and scalable server infrastructure to handle the high volume of messages and media shared on the platform is a significant challenge.
7. Maintenance and Updates
WhatsApp continually introduces new features and security patches. Keeping the clone up-to-date and maintaining compatibility with the latest versions can be time-consuming.
8. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Building a WhatsApp clone involves complying with privacy regulations and ensuring that the app is used responsibly to prevent misuse.
How to Clone a WhatsApp App with ZEGOCLOUD
Building apps like WhatsApp can be a rewarding experience, allowing you to create a personalized messaging platform tailored to your specific needs. However, it’s important to have a solid understanding of the development process and the right tools. One such powerful tool is ZEGOCLOUD, which simplifies integrating in-app messaging into your app. With ZEGOCLOUD’s In-app Chat SDK, you can easily add real-time messaging capabilities, similar to WhatsApp, enabling seamless communication for your users.
The SDK provides a robust infrastructure, ensuring reliable message delivery and real-time synchronization across devices. It supports key features such as one-on-one messaging, group chats, multimedia sharing, push notifications, and read receipts. Additionally, it offers customization options to tailor the chat experience to your app’s unique branding and design.
Preparation
- A ZEGOCLOUD developer account – Sign up
- The latest/updated version of Android Studio
- Android device with version > 6.0
To develop your own WhatsApp Clone using ZEGOCLOUD’s In-app Chat SDK, follow these steps:
Create a new project.
- Launch Android Studio and select the “Create New Project” option.
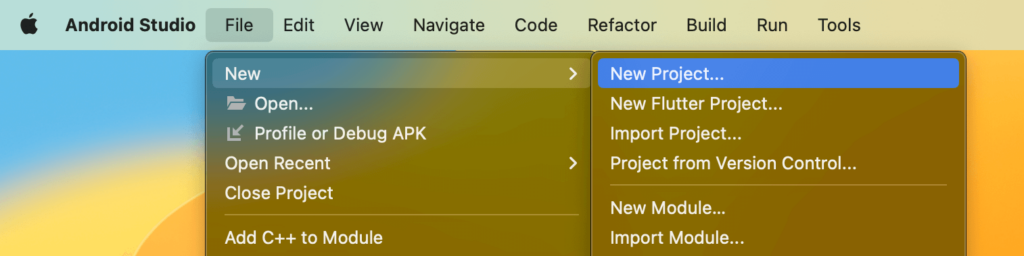
- In the Create New Project dialog, enter the Application Name and select the Project Location.
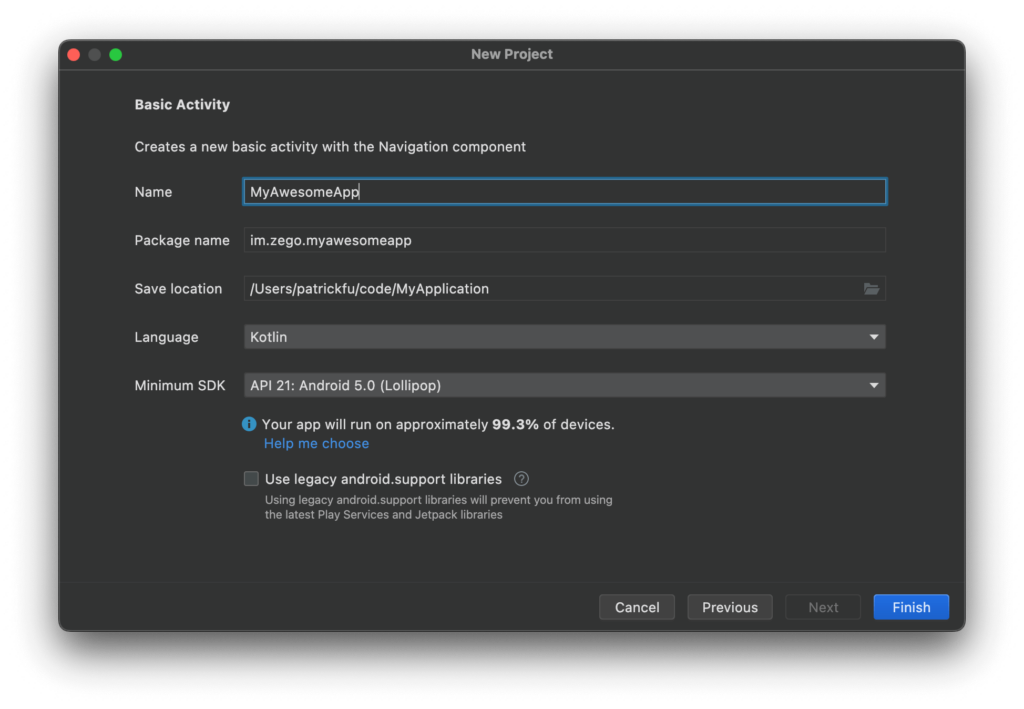
- Leave the Project Type and Language as Empty Activity and Kotlin, respectively. Click Next and then Finish.
Import the SDK
- Download the SDK from the official website.
- Extract the SDK files to your project directory.
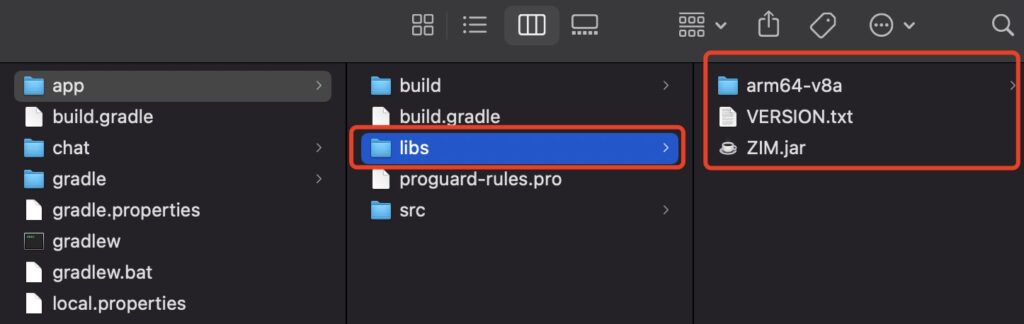
- Open the
app/build.gradlefile and add the necessary contents to integrate the SDK.
Additional configuration
Specify the supported ABIs by adding the ndk node to defaultConfig.
ndk {
abiFilters 'armeabi-v7a', 'arm64-v8a', 'x86_64', 'x86'
}Specify the SDK directory in sourceSets under android.
sourceSets {
main {
jniLibs.srcDirs = ['libs']
}
}Paste the following code into the dependencies node:
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])Adding permissions
To access Android resources, such as the camera and microphone, you need to request permission from the user. You can do this by following these steps:
- Open the
AndroidManifest.xmlfile in theapp/src/maindirectory and add the following code:
<!-- Permissions required by the SDK -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />- To prevent class name obfuscation, add the following codes to your proguard-rules.pro file:
-keep class **.zego.**{*;}Import the class file.
Add the class file to your project.
import im.zego.zim.ZIMCreate a ZIM SDK instance.
To send and receive messages between clients, each client must create a ZIM SDK instance with the AppID obtained in the previous steps.
// Initialize the ZIM SDK with your AppID, AppSign, and Application in Android.
ZIMAppConfig appConfig = new ZIMAppConfig();
appConfig.appID = 12345;
appConfig.appSign = "appSign";
zim = ZIM.create(appConfig, application);Set an event handler object.
Configure event handling before logging in a user. This will allow you to be notified of SDK errors and message-related events.
zim.setEventHandler(new ZIMEventHandler() {
@Override
public void onReceivePeerMessage(ZIM zim, ArrayList<ZIMMessage> messageList, String fromUserID) {
// Define a function to handle incoming one-to-one messages.
}
});Log in to the ZIM SDK.
To send and receive messages, clients A and B must log in to the ZIM SDK.
Here are the steps on how to log in to the ZIM SDK:
- Create a user object using the
ZIMUserInfomethod. - Call the
loginmethod with the user’s information.
// User IDs and usernames must be 32 characters or less and can only contain letters, numbers, and the following special characters: ~!@#$%^&*()_+=&-`;',.<>/\.
ZIMUserInfo zimUserInfo = new ZIMUserInfo();
zimUserInfo.userID = userID;
zimUserInfo.userName = userName;
zim.login(zimUserInfo, new ZIMLoggedInCallback() {
@Override
public void onLoggedIn(ZIMError error) {
// The ZIMError will indicate whether the login was successful.
}
});Send one-to-one messages.
After logging in, clients A and B can send messages to each other by calling the sendPeerMessage method with the recipient’s user ID, message content, and other information. The onMessageSent callback can be used to check the status of a sent message. In this scenario, client A will send a message to client B.
// Exchange private messages.
String toUserID = "xxxx";
ZIMTextMessage zimMessage = new ZIMTextMessage();
zimMessage.message = "Message content";
ZIMMessageSendConfig config = new ZIMMessageSendConfig();
// Set message priority. 1 - Low (by default). 2 - Medium. 3 - High.
config.priority = ZIMMessagePriority.LOW;
// Configure offline notifications.
ZIMPushConfig pushConfig = new ZIMPushConfig();
pushConfig.title = "Offline notification title";
pushConfig.content= "Offline notification content";
pushConfig.extendedData = "Extend information of the offline notification";
config.pushConfig = pushConfig;
zim.sendPeerMessage(zimMessage, toUserID, config, new ZIMMessageSentCallback() {
@Override
public void onMessageSent(ZIMMessage zimMessage, ZIMError error) {
// Add your own code to handle message sending events.
}
});Receive one-to-one messages.
Once Client B logs in, they can receive the message from Client A through the callback onReceivePeerMessage, which is already configured in the setEventHandler method.
zim.setEventHandler(new ZIMEventHandler() {
@Override
public void onReceivePeerMessage(ZIM zim, ArrayList<ZIMMessage> messageList, String fromUserID) {
for (ZIMMessage zimMessage : messageList) {
if (zimMessage instanceof ZIMTextMessage)
{
ZIMTextMessage zimTextMessage = (ZIMTextMessage) zimMessage;
Log.e(TAG, "Received message:"+ zimTextMessage.message);
}
}
}
});Log out
To log out of the ZIM SDK, simply invoke the logout method. It’s a straightforward process that allows you to disconnect from the SDK and end the session.
zim.logout()Destroy the ZIM SDK instance.
To terminate the ZIM SDK instance, use the destroy method. This method ensures the complete closure and cleanup of the SDK instance.
zim.destroy();Run a demo
To see how ZEGOCLOUD’s In-app Chat SDK works, run the sample demo app. For code samples, see the SDK documentation.
Conclusion
Building a WhatsApp clone app for Android is an exciting endeavor that can be made easier and more efficient with the integration of ZEGOCLOUD’s In-app Chat SDK. By leveraging the powerful features and functionalities of the SDK, developers can streamline the development process and create a robust messaging platform tailored to their unique vision and requirements.
Read more:
FAQ
Q1: Is there any clone app for WhatsApp?
Yes, there are several apps available that mimic the look and feel of WhatsApp, but they are not official or authorized by WhatsApp. These “clone” apps typically offer similar features, such as instant messaging, media sharing, and group chats, but often with slight variations or additional functionalities. However, using unofficial WhatsApp clones may not be secure and can lead to privacy concerns.
Q2: How can I clone two WhatsApp?
Cloning WhatsApp on two devices can be done by using dual SIM phones or apps designed to run multiple accounts. On some smartphones, you can use features like “Dual Apps” (on Xiaomi) or “App Twin” (on Huawei) to clone WhatsApp and use two separate accounts. Alternatively, you can use apps like Parallel Space or Dual Space to run multiple instances of WhatsApp.
Q3: How to create a WhatsApp clone?
To create a WhatsApp clone, you would need to develop a messaging app with similar functionalities, such as real-time chat, multimedia sharing, notifications, and end-to-end encryption. You can use development platforms like ZEGOCLOUD to integrate messaging and video call features quickly. Building a clone requires knowledge of mobile app development (using Flutter, React Native, or Java/Kotlin for Android, Swift for iOS) and server-side technologies.
Q4: Can WhatsApp be cloned on two phones?
Officially, WhatsApp does not allow the use of a single account on two phones. However, you can access your WhatsApp account on multiple devices by using WhatsApp Web or WhatsApp Desktop, which syncs with your main device. If you want to use WhatsApp on two phones, you would need to set up a second account with a different phone number or use a dual SIM phone to run two WhatsApp accounts.
Let’s Build APP Together
Start building with real-time video, voice & chat SDK for apps today!