Insert local messages
Overview
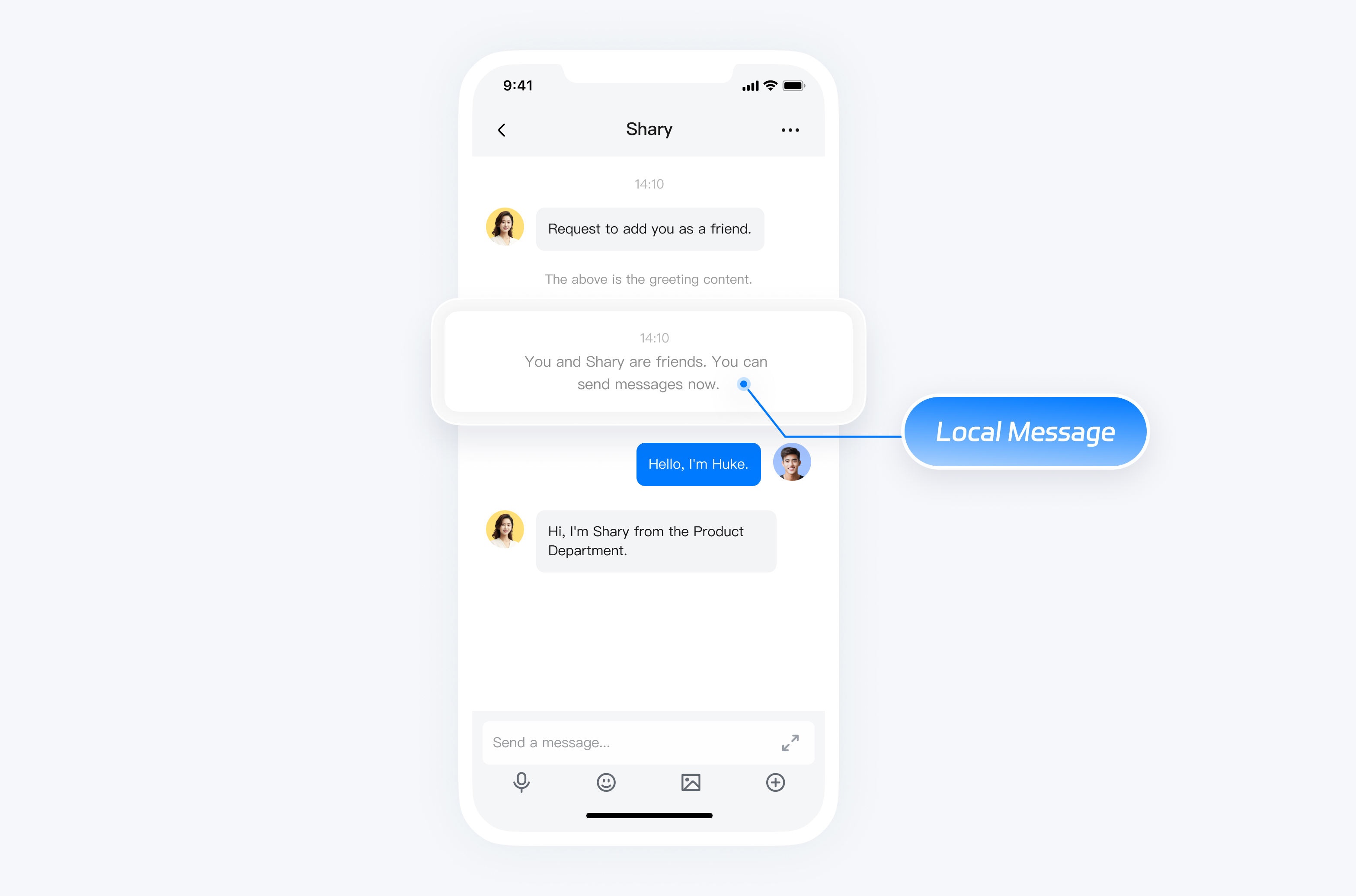
The ZIM SDK supports inserting local messages into one-on-one and group conversations, and starting from version 2.13, it also supports inserting local messages into room conversations. The inserted messages will only exist locally on the device and will not be sent to other users or synchronized to other devices. Additionally, these messages will not be retained after uninstalling the client application.
You can use this feature to insert a message into the local database for displaying system notifications. For example, it can be used for local notifications such as joining or leaving a group, which do not need to be sent to other users across devices.
- The ZIM SDK currently supports inserting local messages for "peer/group" conversations but does not support inserting local messages for "room" conversations.
- The ZIM SDK does not support inserting signaling messages.
Implementation process
To insert a message into the local database, you need to call the insertMessageToLocalDB API and introduce the created ZIMMessage message, conversationID, conversationType, senderUserID, and other parameters.
Sample code
// Insert a message into the local database.
// Inserting a custom message is used as an example here. You can also insert other types of messages. However, signaling messages are not supported.
String message = "custom";
int subType = 1; // The custom system message type defined by the business, with values ranging from [0,200].
ZIMCustomMessage customMessage = new ZIMCustomMessage(message,subType);
String conversationID ="conversationID";
String senderUserID = "senderUserID";
ZIMConversationType type = ZIMConversationType.PEER;
zim.insertMessageToLocalDB(customMessage, conversationID, type, senderUserID, new ZIMMessageInsertedCallback() {
@Override
public void onMessageInserted(ZIMMessage message, ZIMError errorInfo) {
// You can listen for whether the insertion is successful through this callback.
}
});// Insert a message into the local database.
// Inserting a custom message is used as an example here. You can also insert other types of messages. However, signaling messages are not supported.
String message = "custom";
int subType = 1; // The custom system message type defined by the business, with values ranging from [0,200].
ZIMCustomMessage customMessage = new ZIMCustomMessage(message,subType);
String conversationID ="conversationID";
String senderUserID = "senderUserID";
ZIMConversationType type = ZIMConversationType.PEER;
zim.insertMessageToLocalDB(customMessage, conversationID, type, senderUserID, new ZIMMessageInsertedCallback() {
@Override
public void onMessageInserted(ZIMMessage message, ZIMError errorInfo) {
// You can listen for whether the insertion is successful through this callback.
}
});Sample code
// Insert a message into the local database.
// Inserting a custom message is used as an example here. You can also insert other types of messages. However, signaling messages are not supported.
ZIMCustomMessage *customMessage = [[ZIMCustomMessage alloc] init];
customMessage.message = @"custom";
customMessage.subType = 1; // The custom system message type defined by the business, with values ranging from [0,200].
NSString *conversationID = @"conversationID";
ZIMConversationType type = ZIMConversationTypePeer;
NSString *senderUserID = @"senderUserID";
[self.zim
insertMessageToLocalDB: customMessage
conversationID:conversationID
conversationType:type
senderUserID:senderUserID
callback:^(ZIMMessage *_Nonnull message, ZIMError *_Nonnull errorInfo) {
GGLog(@"errorcode", errorInfo.code);
}];// Insert a message into the local database.
// Inserting a custom message is used as an example here. You can also insert other types of messages. However, signaling messages are not supported.
ZIMCustomMessage *customMessage = [[ZIMCustomMessage alloc] init];
customMessage.message = @"custom";
customMessage.subType = 1; // The custom system message type defined by the business, with values ranging from [0,200].
NSString *conversationID = @"conversationID";
ZIMConversationType type = ZIMConversationTypePeer;
NSString *senderUserID = @"senderUserID";
[self.zim
insertMessageToLocalDB: customMessage
conversationID:conversationID
conversationType:type
senderUserID:senderUserID
callback:^(ZIMMessage *_Nonnull message, ZIMError *_Nonnull errorInfo) {
GGLog(@"errorcode", errorInfo.code);
}];Sample code
// Insert a message into the local database
// Here is an example of inserting a custom message, you can modify it to insert other types of messages, signaling messages are not supported.
std::string conversationID="conversationID";
std::string sender_user_id = "sender_user_id";
zim::ZIMConversationType type = zim::ZIMConversationType::ZIM_CONVERSATION_TYPE_PEER;
int subType = 1; // The system message type defined by the business, with values ranging from [0, 200]
auto customMessage = std::make_shared<zim::ZIMCustomMessage>("custom message", subType);
zim_->insertMessageToLocalDB(std::static_pointer_cast<zim::ZIMMessage>(customMessage), conversationID, type, sender_user_id, [=](const std::shared_ptr<zim::ZIMMessage> &message, const zim::ZIMError &errorInfo) {
// You can listen to the callback of inserting messages here
});// Insert a message into the local database
// Here is an example of inserting a custom message, you can modify it to insert other types of messages, signaling messages are not supported.
std::string conversationID="conversationID";
std::string sender_user_id = "sender_user_id";
zim::ZIMConversationType type = zim::ZIMConversationType::ZIM_CONVERSATION_TYPE_PEER;
int subType = 1; // The system message type defined by the business, with values ranging from [0, 200]
auto customMessage = std::make_shared<zim::ZIMCustomMessage>("custom message", subType);
zim_->insertMessageToLocalDB(std::static_pointer_cast<zim::ZIMMessage>(customMessage), conversationID, type, sender_user_id, [=](const std::shared_ptr<zim::ZIMMessage> &message, const zim::ZIMError &errorInfo) {
// You can listen to the callback of inserting messages here
});Sample code
// Insert a message into the local database.
// Inserting a text message is used as an example here. You can also insert other types of messages. However, signaling messages are not supported.
const message: ZIMMessage = { type: 1, message: 'string' };
const conversationType = 0;
zim.insertMessageToLocalDB(
message,
'conversationID',
conversationType,
'senderUserID'
).then((res) => {
// You can listen for whether the insertion is successful.
});// Insert a message into the local database.
// Inserting a text message is used as an example here. You can also insert other types of messages. However, signaling messages are not supported.
const message: ZIMMessage = { type: 1, message: 'string' };
const conversationType = 0;
zim.insertMessageToLocalDB(
message,
'conversationID',
conversationType,
'senderUserID'
).then((res) => {
// You can listen for whether the insertion is successful.
});Sample code
// Insert a message into the local database
// Here we demonstrate inserting a custom message, developers can modify it to insert other types of messages, signaling messages are not supported.
String message = "custom";
int subType = 1; // The system message type defined by the business, with values ranging from [0, 200]
ZIMCustomMessage customMessage = new ZIMCustomMessage(message,subType);
String conversationID ="conversationID";
String senderUserID = "senderUserID";
ZIMConversationType type = ZIMConversationType.PEER;
zim
.insertMessageToLocalDB(message, conversationID, type, senderUserID)
.then((value) {
})
.catchError((onError) {
});// Insert a message into the local database
// Here we demonstrate inserting a custom message, developers can modify it to insert other types of messages, signaling messages are not supported.
String message = "custom";
int subType = 1; // The system message type defined by the business, with values ranging from [0, 200]
ZIMCustomMessage customMessage = new ZIMCustomMessage(message,subType);
String conversationID ="conversationID";
String senderUserID = "senderUserID";
ZIMConversationType type = ZIMConversationType.PEER;
zim
.insertMessageToLocalDB(message, conversationID, type, senderUserID)
.then((value) {
})
.catchError((onError) {
});Sample code
// Insert a message into the local database
// Here is an example of inserting a custom message, you can modify it to insert other types of messages (signaling messages are not supported).
int subType = 0; // Custom message type defined by the business, with a value between 0 and 200
ZIMCustomMessage customMessage = new ZIMCustomMessage("message", subType);
string conversationID = "conversationID";
string senderUserID = "senderUserID";
ZIMConversationType type = ZIMConversationType.Peer;
ZIM.GetInstance().InsertMessageToLocalDB(customMessage, conversationID, type, senderUserID, (ZIMMessage message, ZIMError errorInfo) =>
{
// You can listen to this callback to check if the message is inserted successfully
});// Insert a message into the local database
// Here is an example of inserting a custom message, you can modify it to insert other types of messages (signaling messages are not supported).
int subType = 0; // Custom message type defined by the business, with a value between 0 and 200
ZIMCustomMessage customMessage = new ZIMCustomMessage("message", subType);
string conversationID = "conversationID";
string senderUserID = "senderUserID";
ZIMConversationType type = ZIMConversationType.Peer;
ZIM.GetInstance().InsertMessageToLocalDB(customMessage, conversationID, type, senderUserID, (ZIMMessage message, ZIMError errorInfo) =>
{
// You can listen to this callback to check if the message is inserted successfully
});